API testing is one of the most complex yet significant steps in software development that comes as a part of QA testing. There are many benefits of API testing since those can be sophisticated and they frequently depend on protocols and standards that are hard to find in other forms of testing.
While developers prefer to test just the core functionality they are working on, QA testers need to adopt API testing methodology to evaluate functionality, API performance tests, and API security tests. They check whether all components operate together from end to end.
Starting the API testing
To begin an API testing process, it is essential to have a clear knowledge of API testing methodologies’ scope and purpose.
Here are some basic questions to consider before starting any API tests.
- What kinds of endpoints can you put to the test?
- When a request is successful, what are the anticipated response codes?
- If a request is denied, what response codes should be expected?
- What error message should be generated when a request is failed?
Once you have proper answers to the questions mentioned above, you can start adopting different testing approaches. The software development services should also check over the API testing to determine what situations or variables testers can assess and whether a certain system works properly and reacts appropriately? This is where test cases come in.
After that, to drive the advantages of API testing, you can conduct tests and compare their predicted outcomes with their actual outcomes.
Your tests should analyze the following response:
- Reply time
- Data quality
- Confirmation of authorization
- HTTP status code and
- Error codes
Why API testing is important?
API testing plays a significant role in software systems as it validates how applications communicate and exchange data. Businesses can confirm that their APIs work reliably across various scenarios by using structured API testing methodologies.
This testing focuses on detecting errors that could disrupt processes makes sure that there is smooth integration between systems. A reliable Application Programming Interface testing strategy can minimize risks and maintain system stability.
API testing is damn critical for ensuring smooth communication between systems and delivering reliable functionality. Up next, we will look at the specific aspects tested to maintain performance and security.
What exactly do we check during API testing?
When testing APIs, various aspects are evaluated to confirm they function correctly. These include:
- Data accuracy: Checking whether APIs return data in the expected format.
- Response times: Ensuring that APIs respond promptly under all conditions.
- Security: Verifying that sensitive information remains protected.
- Error handling: Testing how APIs behave when unexpected inputs are provided.
- Integration: Confirming compatibility across multiple platforms and devices.
Using the best tools and techniques ensures thorough validation while automating repetitive tasks.
Benefits of API testing
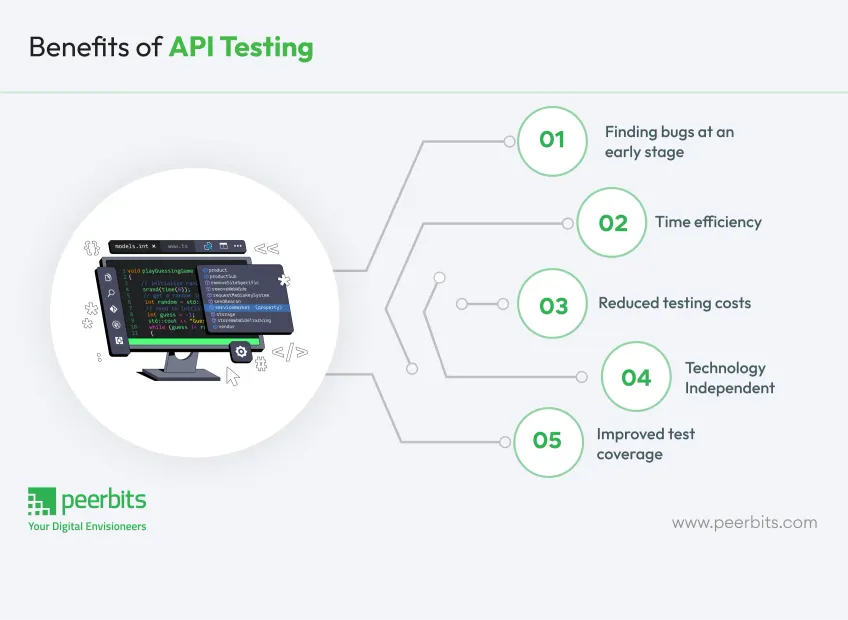
There are many advantages of API testing that surpass the benefits of GUI testing, ensuring efficiency in testing and the ability to deploy software quicker with lowered testing expenses. Here are some of the key benefits of API testing to consider.
1. Finding bugs at an early stage of software development
It is possible to test APIs without a user interface. That is, they may perform tests without testing the full software. This means a developer can detect different types of bugs early in API testing before those errors affect GUI.
The benefit of such API testing is that the businesses opting for quality assurance and control services save time and money.
2. Effective use of time
One of the advantages of API testing is that it takes less time than functional GUI testing, as the latter involves polling of web page components which takes much time.
If you want to know how much time API testing can save by testing the core functionality of your application, then here is a quick comparison.
“3,000 API tests in 50 minutes (in parallel execution) will take 3,000 GUI tests in 30 hours (in parallel execution)
You should expect similar time reductions for your QA UI testing team. Choosing from the range of API testing methodologies ensures better and quicker test coverage than automated GUI tests. It is because API test automation requires less code.
3. Reduced testing costs
Before doing GUI tests, it is useful to test the application’s API level functionality. Early error detection minimizes manual testing costs while also expanding the test coverage.
The benefit of API testing is that the test automation is quicker and more accurate than GUI test automation, resulting in fewer hours and reducing the cost of software testing.
4. Non-attachment to programming languages
Your API testing methods involve exchanging data in XML or JSON formats. This data transport method is independent of application language, enabling QA engineers to use any programming language that offers these technologies to automate API testing, including PHP, Ruby, Java, JavaScript, and more.
5. Improved test coverage
An automated API test may cover a far wider range of functionality than unit tests constrained to only functional components within a particular application. This is where the majority of issues emerge.
Tests at the API level, on the other hand, are aimed at ensuring that all system components work as intended. The benefit of such API testing is that it helps improve the program’s overall quality and contributes to improved user experiences.
API testing provides reliability, security, and smooth integration, making it indispensable for robust software systems. Next, let’s address the key challenges that arise during API testing and how to navigate them effectively.
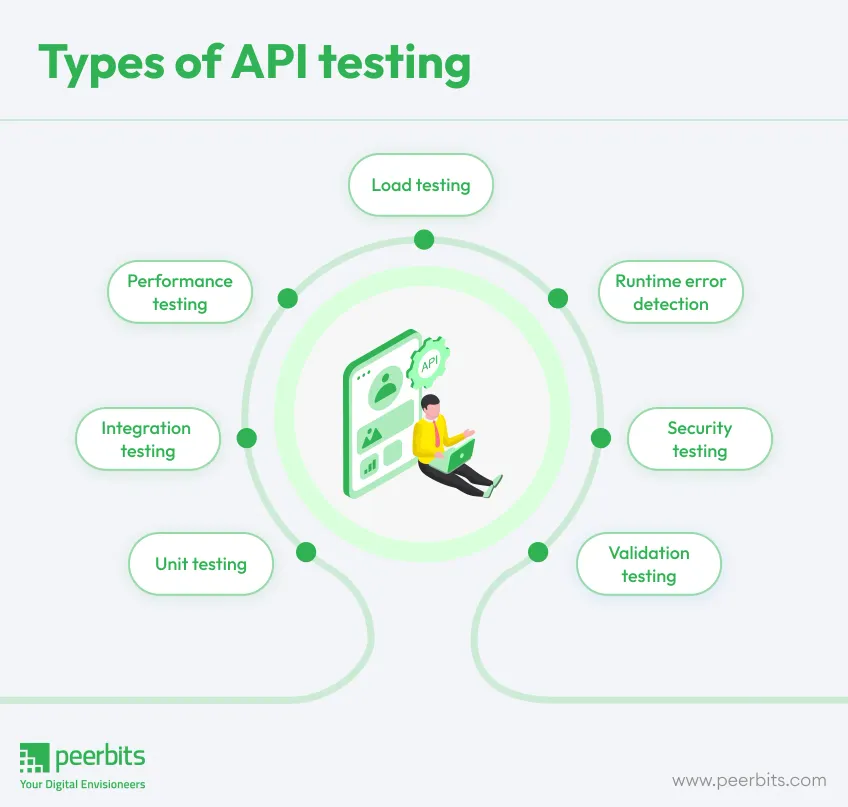
Types of API testing
It’s been a long journey for APIs that began as basic libraries of code that programs could use to operate on the same machine to the more sophisticated remote APIs that let programs on one computer call up programs on another.
Specialty tests abound, and no list could have it all included, but these are the seven major types of API testing that the QA team may use.
Unit testing
The term “unit testing” refers to creating API tests that run with each new version of an application. To pass a build of the program, they should be written near to the code.
How much code coverage does API need depends on its risk level and the functions it provides?
It is important to consider this API testing area because it will support the remainder of the work in the future.
Integration testing
Effective API integration testing is necessary to stay prepared in advance. It’s essential that API integration testing is performed to ensure that your product’s functionality is not compromised.
The app’s functioning mostly determines the user experience. How the user feels about your product determines whether or not it’s a success or failure.
As a result of its scope, structure, and constant development, API integration tests are challenging and divisive. On the other hand, the benefits include faster production of higher-quality goods, making it a challenge to take on.
Performance testing
This API performance test aims to examine the program’s reaction time, dependability, speed, and functionality. As a result, this assures maximum efficiency. Specifically, this test aims to eliminate software performance bottlenecks rather than flaws.
Load testing
This is a non-functional test that helps determine the performance of a software application or product. End-to-end API testing in software development is published in a real-time environment where several users may test it simultaneously.
Load testing assists the developer in understanding the program’s running capabilities, examining the application’s sustainability while several users are using it, and identifying the application’s potential to grow to accommodate additional users.
Runtime error detection
This is a powerful method to monitor and oversee an app that uses glitch-hunting techniques, such as human or automated testing. Resource leaks, exceptions, and so forth are all examples of this.
The test may provide reliable findings in terms of bug discovery if it is done with the greatest care. You can focus on particular features like monitoring, error detection, execution faults and any probable leaks, these tests are your best shot at uncovering severe flaws.
Security testing
This test guarantees that the API testing in software development coupled with implementation is protected from external dangers. Moreover, other procedures like validation of encryption methods and the design of API access control are included in API security testing. In addition, it handles user rights and verifies authorizations.
Validation testing
Validation testing is one of the most critical tests performed at the last stage of product development. It examines the product, behavior, and overall efficiency.
When it comes to API app development, validation testing may be considered a guarantee that the product is being developed correctly.
The different types of API testing play an important role in ensuring APIs function as expected. Next, we’ll look at the types of bugs that API testing can detect to further improve system stability.

How to do API testing?
Testing APIs (application programming interfaces) is done at the message layer without the need for a user interface. When starting the API testing, the QA team uses it to see whether APIs live up to their expectations in terms of functionality, dependability, speed, and security.
Your product architecture API testing should include the following ways to start the API testing.
Gathering API requirements
It is necessary to gather the API’s requirements before testing. You may use API to API comparison or database verification to evaluate input and output data, depending on where and how an API fits into the overall application process.
Discovery testing
API integration and API performance tests are impossible without API discovery. When it comes to API discovery, QA engineers need to find the tiniest of elements that make everything work as it should.
At this stage of API discovery, you should figure out the best way to get to API testing in the first place.
Choosing the right API testing methodology can help reduce and eliminate the amount of API noise in various applications, software, and websites even in Python API development. To verify API calls defined in R&D and client requirements, the discovery step requires human execution of API calls.
Define the API requirements
Writing good requirements is very hard. Therefore, it needs open communication to define proper requirements as every stakeholder can have useful input on the requirements. Also, they may pose some tough questions that need answering.
This is why teamwork matters — developers, testers, system architects, analysts, product owners, they all know their domain best and should be included in creating requirements.
For this, a cohesive brainstorming session is needed to answer key questions like;
- How are you going to use this API?
- What are the ways through which the application can handle data?
- How to handle system failure?
- How can the system handle output?
- What are the options for the system to handle unexpected input?
- What fields does the API transmit and receive?
- How will the API communicate with other APIs, including the protocol to be used?
- Criteria for admission and exit.
- The API/pass/fail feature’s criterion.
Data input → output → outcome validation and verification
Compared to managing the quantity of test data created and subsequently confirmed, each of these activities is relatively easy. Methods for verifying test data may be challenging and make or break an API and application’s testing process. API testing automation can be useful here.
Managing failures: Validation, fixes, and retesting
- Future, you need to create a testing environment that’s as close to real-world conditions as feasible.
- Ensure including documentation review; this is also known as static API testing since we are evaluating documentation that will never be performed.
- Use one API request as a proof of concept before diving into it and making sure all your scripts are functional.
- Carry fuzz testing and all other functional testing that includes briefing on which tests will be conducted at what level. This is the step to plan all your tests.
- In order to speed up testing, you can create stubs and drivers in advance of the whole environment’s integration.
- End-to-end testing requires API integration with the whole environment and running the test cases.
- Always verify if test results meet the specifications. A single failed test doesn’t mean the entire feature should be rejected but requires a thorough investigation and risk assessment.
- Make any necessary fixes and retest all of the features that have failed.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) should begin only when all the criteria are met.
- If needed, perform any fixes and retest the feature that failed.
- Once the test documentation is complete and the criteria are met, the QA lead will approve the feature and will allow it to be implemented live.
- Also, it is recommended to run a sanity check prior to releasing the final version.
- Check any logs you have or prospective service desk instances to see if there are any issues with your production releases.
Top tools for the API testing
When it comes to API testing, there are multiple API testing methods and, similarly, an array of API testing tools depending on your testing requirements, budget, and technology.
Here are some of the top API testing tools you may consider before running any API tests.
1. Postman
Initially, Postman was a Google Chrome extension. Postman API testing tool service is now available on both Windows and Mac, providing a great option for exploratory and manual testing.
You can use the Postman REST API testing tool for API testing set up for automated tests and troubleshoot the same.
Top features
- Tools, collections, and workspaces are all included.
- In addition to RAML and Swagger, you can use Postman with various formats.
- Postman’s UI makes it easy to extract data from online APIs.
- It doesn’t rely on the command line to write Boolean tests.
2. REST-assured
Thanks to this free and open-source Java Domain-Specific Language, testing REST services has never been easier. You can run validation and verification of the responses to these queries using this tool.
When testing RESTful services in Java, you should use Rest-assured API testing. It is a great open-source platform that provides Java domain-specific languages for testing REST services. Also, it is commonly used to test JSON and XML-based applications.
Top features
- Integrates with Serenity automation framework seamlessly.
- Users don’t have to write any code because of the pre-existing functionality.
- It provides a variety of ways to test and verify a secure API.
- Given/When/Then test notation is supported by the use of Fluent API, making your tests more human-readable right away.
- No matter which API testing methods you follow, it can handle all HTTP methods and a few specific instructions, such as POST and GET.
3. Katalon Studio
QA experts can rely on Katalon studio to automate API, web, desktop, and mobile testing. This tool simplifies deployment by incorporating all frameworks, ALM connectors, and plugins into a single package for quick deployment.
A few of the key advantages of Katalon studio include its ability to combine UI and API/Web services for several platforms (Windows, Mac OS, and Linux).
Top features
- API automation testing is made easier with the help of this powerful integrated development environment (IDE).
- All REST and SOAP requests are supported.
- Swagger, Postman, and WSDL test requests may be imported.
- It may be run locally and remotely, with real-time analysis.
- Simple request composition with numerous data sources thanks to data-driven (e.g. XLS, CSV).
4. SoapUI
This API testing tool is headless, and therefore it can be used to test both SOAP and REST APIs and web services. For this reason, it is frequently chosen by testers as one of the most useful tools for asynchronous testing based on complex scenarios.
Additionally, it is notable for its excellent data-driven testing and user-friendliness.
Top features
- With SoapUI, you have a slew of enterprise-level capabilities. For instance, you get the MockService and its methods generated for you automatically from a WSDL that you provide.
- SoapUI helps sophisticated test scenarios without writing any scripts with its drag & drop functionality. You can also add test suites to a project once you create it.
- Once you conduct a load test, the LoadUI generates a report that helps assess the application’s load capacity. Use SoapUI to create complex load tests from functional API tests simply.
- You can test APIs using data supplied from files, databases, and Excel, allowing them to replicate how users interact with the APIs.
- Enables asynchronous testing and native CI/CD integrations.
5. Paw
You may use the Paw tool to inspect and explain the APIs you create or acquire. Calls may be made using the app’s native macOS interface, and it can test server responses, generate client passes, and introduce new APIs.
Paw is a complete, one-stop-shop for testing and describing APIs on the Mac when it comes to testing and describing APIs. You can create HTTP requests, examine the server’s response, and even produce code with this feature-rich and well-designed Mac tool.
Top features
- Analyze API capability for Mac centering by delivering all forms of HTTPS requests to API.
- Use JSON Schema to identify and clarify the type of API tester being used.
- Connection buttons are enabled without compromising the user’s capacity to collaborate.
- Using API, users can find leggings and then using Paw, a network of users can work together to make improvements.
Types of bugs that API testing detects
API testing uncovers a range of issues that might otherwise disrupt application functionality. These include:
- Data issues: Incorrect formatting or mismatched data parameters.
- Performance problems: Delays or failures under heavy usage.
- Security flaws: Weak access controls or data breaches.
- Logic errors: Failures to return expected outputs based on input.
When you hire dedicated developers, they can effectively refine APIs by detecting such bugs early on and deliver a reliable and secure system.
Challenges of API testing
API testing can face difficulties such as unstable server environments or dependencies on external APIs. These interruptions can delay the testing process and lead to incomplete validations.
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Unstable environments | Invest in environment virtualization to simulate consistent conditions during testing. |
| Rapid API updates | Maintain a dynamic framework that adapts to frequent API changes with minimal rework. |
| Dependency on external APIs | Use mock servers to replicate external API behavior and reduce reliance on live systems. |
| Complex workflows | Break workflows into smaller, testable units to streamline validation processes. |
| Security validations | Implement continuous security monitoring to identify vulnerabilities early. |
| Handling different API methods | Develop method-specific test cases that address unique requirements for GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE operations. |
Challenges in testing different API methods
Each API method, such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, presents unique hurdles. For GET methods, it is essential to validate data retrieval without errors.
POST testing involves ensuring that data submission works as intended, while PUT and DELETE require verification to prevent unintended alterations or removals. APIs often depend on authentication layers or rate limits, which must also be validated during testing.
Utilizing advanced API testing methodologies can simplify these complexities and improve accuracy.
API in SaaS product development
APIs are critical for API in SaaS product development, powering features, integrating third-party tools, and scaling efficiently. Thorough API testing methodologies confirm that APIs function properly, helping SaaS platforms deliver smooth workflows and better user experiences.
Testing focuses on verifying data exchange, examining integration points, and validating security layers. Effective API testing in SaaS product development supports platforms in meeting user demands while maintaining consistent performance.
Conclusion
API testing is becoming a tough notion in the software and QA testing chain when it comes to verifying the software or an application. If you face any difficulty in getting assured execution, then speak to QA experts at Peerbits.
We work to improve our platform and procedures to elevate the testing experience to an altogether new level, providing a greater degree of client satisfaction.
At Peerbits, we provide a range of testing services as a part of full-fledged mobile app development services. Our expert QA team performs test case-based testing to make your apps secure & future-ready.

FAQs
In custom software development services, API testing evaluates the compatibility, reliability, and security of APIs. It ensures that APIs integrate smoothly with unique workflows, improving the adaptability of the software for business-specific use cases.
Enterprises can optimize API security testing by integrating authentication protocols, encryption techniques, and regular vulnerability assessments. This reduces the risk of breaches and protects business data.
Structured API testing verifies data flow and component interactions, which is critical for IoT in manufacturing systems. It supports real-time data exchange, enhances automation, and secures sensitive manufacturing data, ensuring efficient system functionality.
Businesses should use advanced API performance tests that simulate high-traffic scenarios, identify bottlenecks, and validate response times. Automation tools and monitoring systems are critical for handling large-scale operations.
Continuous testing lets businesses identify and address performance issues in real time. For scalable applications, it ensures APIs can handle growth in user demands and maintain consistent operation across diverse environments.
API testing methodologies ensure that APIs are functional, reliable, and secure. For Python API development, they help startups and enterprises build scalable solutions that meet both operational demands and market needs.








