Choosing modern healthcare comes with managing terabytes of patient data, connected IoT devices, and 24/7 care. On top of that, every surge in data or demand turns into a threat when your systems run on outdated or legacy infrastructure.
Just a few months back, in April 2025, Yale New Haven Health System in Connecticut suffered a breach affecting over 5.5 million patients.
The attack exposed personal details such as names, contact information, and Social Security numbers of the patients.
Even after the breach, YNHHS confirmed that electronic medical records were not compromised. Such an incident is a proven example where digital health data, when managed properly, can still be protected, as compared to legacy-led data.
These events underline why more healthcare providers are moving to flexible, compliant systems built on trusted cloud services and solutions. What should be the goal? Just better performance? Or a healthcare system that performs better, has stronger security, easier compliance, and better support for connected healthcare.
Without proper structure, Cloud migration can lead to downtime or even violations. And with the right cloud migration strategy, it can improve healthcare delivery, system performance, and long-term agility.
So, what now? We’ll look at the major healthcare cloud migration challenges teams face and what you can do to avoid them with clarity and control.
Why choose healthcare cloud migration?
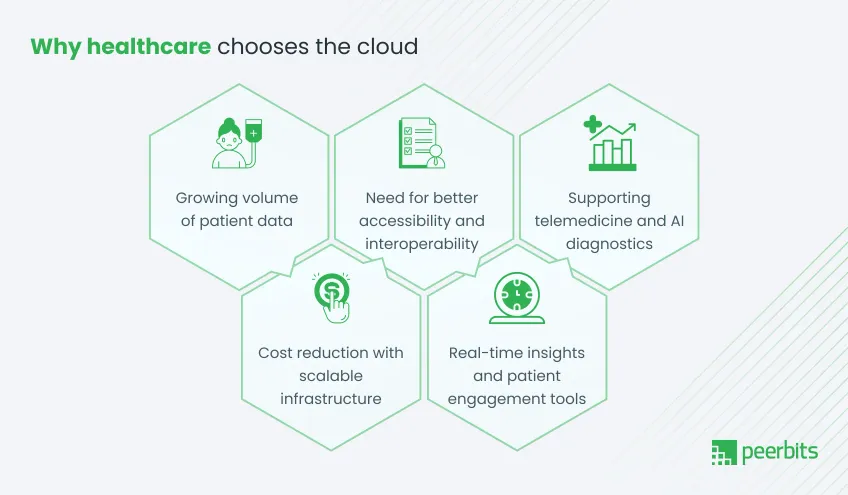
If your infrastructure feels like it is lagging behind patient demands or system requirements, you are not alone. Yes, more healthcare providers are now moving to cloud-based healthcare solutions that can scale faster, connect better, and support smarter care.
Here’s why:
1. Growing volume of patient data
EHRs, imaging files, wearable data, and remote patient monitoring systems are creating large volumes of clinical data. Traditional servers often hit limits quickly. Healthcare cloud migration supports scalable storage and faster access without constantly upgrading hardware.
2. Need for better accessibility and interoperability
Healthcare teams need quick and secure access to records, across departments or locations. Cloud systems improve healthcare data interoperability, making it easier to share data between EHRs, labs, pharmacies, and external care networks.
3. Supporting telemedicine and AI diagnostics
Cloud infrastructure plays a strong role with video healthcare consultations, AI-powered image analysis, and Telemedicine app. With the right cloud services provider, you can bring support to real-time patient care without performance issues.
4. Cost reduction with scalable infrastructure
Cloud models help you scale usage based on your demand. That means less spending on servers, software licenses, or maintenance. You only use what you need, which makes it easier to control IT budgets over time.
5. Real-time insights and patient engagement tools
From dashboards to patient portals and m health apps, cloud platforms make it easier to create meaningful interactions. With strong Cloud services and solutions for healthcare, you can bring visibility to both staff and patients in real time.
Now that you have seen why so many healthcare providers are making this move, let’s look at what might hold you back during the actual migration process.

Cloud migration challenges and solutions in healthcare systems
Migrating your healthcare systems to the cloud brings long-term benefits, but the process is complex. Challenges appear around privacy laws, legacy systems, stakeholder coordination, and continuity of care.
Below are the key problem areas and practical solutions to help your teams navigate them more confidently.
1. Navigating regulatory compliance and data privacy

-
Healthcare data is governed by strict privacy laws, which can differ across regions.
-
Standards like HIPAA, GDPR, NHS IG Toolkit, and PDPA define how data should be stored and accessed.
-
Misconfigured access controls can create audit violations or patient privacy risks.
-
Multi-region hosting requires clarity around where data lives and how it’s managed.
-
Vendors without certifications like HITRUST or ISO 27001 can create compliance gaps.
Solution:
Document your compliance requirements by region before the migration starts. Select vendors with the necessary healthcare certifications. Make cloud strategies to assess risks and help design your architecture with built-in compliance. Experienced teams offering HIPAA-compliant cloud solutions will help you avoid delays and rework later.
2. Risk of service disruption during migration

Live systems often get affected if the migration plan lacks structure.
- Downtime can delay reports, billing, or patient care.
- Misalignment between migration and operations can affect timelines.
- Lack of a sandbox leads to untested configurations being deployed.
- Without a rollback plan, recovery takes longer when things go wrong.
Solution:
Use a staged migration plan with sandbox environments for testing. Deploy with controlled timelines, starting with non-critical applications. Consider blue/green rollouts or a hybrid cloud for healthcare setup for smoother transitions. Teams offering cloud consulting services can help you plan rollback options and support coordination across vendors and departments.
3. Data integration and interoperability concerns

Migration often reveals gaps in how systems connect and share data.
- Many organizations still rely on legacy EHR and PACS that are not designed for cloud use.
- Proprietary formats from multiple vendors can lead to data silos.
- Older APIs may not support HL7 or FHIR, blocking real-time sharing.
- Delays in access to records or diagnostics slow down care workflows.
Solution:
Start with a compatibility assessment across your platforms. Include healthcare data interoperability in your cloud roadmap. Choose cloud platforms and tools that support modern data exchange standards.
4. Managing stakeholder concerns and resistance

Cloud migration affects everyone in your organization. Without preparation, resistance may slow progress.
- Doctors and admin staff may be hesitant to change their routines.
- Leadership may need clarity on value, costs, and timelines.
- Some teams may not have enough technical support to make the transition.
- Compliance and technical teams might work in silos with different goals.
Solution:
Involve key roles early. Organize workshops and share migration benefits tailored to each team. Offer hands-on training before rollout. Take help of your cloud partner to guide internal change management, define roles, and support coordination between departments. This helps create a shared roadmap that keeps the project on track.
Best practices for healthcare cloud migration
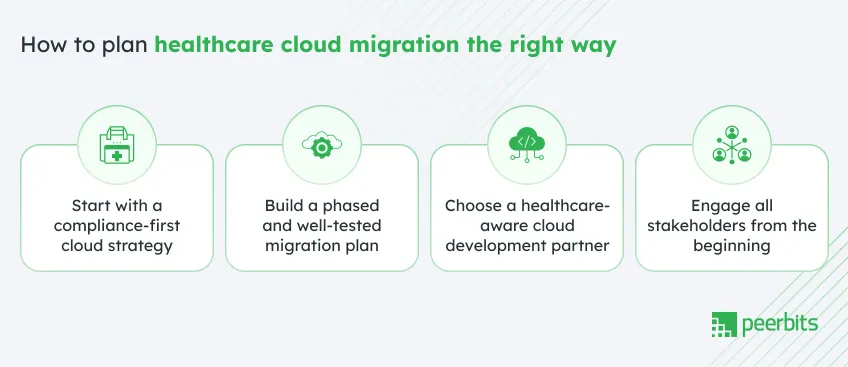
A successful healthcare cloud migration depends on how you prepare, not how fast you migrate. If your systems involve clinical data, user-sensitive workflows, or strict regional regulations, then each step needs structure and clarity.
Here are cloud migration best practices that can help your teams reduce disruption and stay in control throughout the migration process.
1. Start with a compliance-first cloud strategy
Your migration plan should begin with security and compliance. These aren't post-deployment checks. They form the foundation of your system design.
-
Begin by mapping the regions where you operate and the regulatory standards you must follow. This could include HIPAA, HITRUST, GDPR, or PDPA.
-
Choose vendors that specialize in cloud managed services for healthcare. Examples include AWS HIPAA Eligible Services, Microsoft Azure Healthcare APIs, and Google Cloud Healthcare Data Engine.
-
Implement audit trails and access logs from the beginning to keep records of every action across your cloud environment.
Teams that treat compliance as a setup task, not a safeguard, often avoid the most common regulatory setbacks.
2. Build a phased and well-tested migration plan
Migrations that follow a phased path are easier to manage and less likely to cause service gaps.
- Set up shadow environments that mirror production so you can test configurations before rollout.
- Begin with non-critical applications to reduce early-stage pressure.
- Plan your stages with go-live timelines that work with your clinical and operational needs.
- For every stage, define a backup process that lets you restore systems quickly in case of rollback.
- In many cases, using a hybrid cloud for healthcare or a blue/green deployment model helps keep core services running while new ones go live.
This approach improves visibility, reduces patient risk, and helps your teams stay in sync during the transition.
3. Choose a healthcare-aware cloud development partner
Not all vendors understand what healthcare systems require. You need more than infrastructure support. You need domain familiarity.
- Prioritize partners with a background in healthcare software development, EHR integrations, FHIR APIs, and HIPAA-compliant environments.
- Ask for case studies that include usage metrics, timelines, and system performance after deployment.
- Avoid vendors who have only built generic infrastructure with no exposure to clinical workflows.
- Look for partners who provide monitoring and support after deployment, even after the build phase.
Your vendor should understand both the technical requirements and how they affect Healthcare environments.
4. Engage all stakeholders from the beginning
Migration impacts the entire organization. Technical upgrades will fail if users are not informed, trained, or aligned with the roadmap.
- Bring in clinicians and administrative staff during early-stage planning. Their feedback will help shape workflows that work in practice, not just on paper.
- Set up training sessions and walk-throughs before rollout to make the learning process less disruptive.
- Create short role-based briefs that show how each team will benefit from faster imaging access to fewer login issues.
- Confirm that IT, operations, compliance, legal, and finance teams are fully aligned on priorities, scope, and approval checkpoints.
With clear communication, internal resistance becomes easier to manage, and system adoption improves.
What to check before cloud migration in healthcare
Ask yourself these before you start:
- Have you listed and addressed all compliance needs based on location?
- Will your current systems work with FHIR APIs and EHR integrations?
- Is your cloud partner experienced in healthcare environments and workflows?
- Do you have a clear rollback plan if performance drops or data loss occurs?
- Are users across departments trained and aligned with the cloud migration services plan?
If your answer is “yes” to all five questions, your project is ready to begin.
Conclusion
Migrating healthcare systems to the cloud supports better data management, improved system performance, and long-term scalability. As patient needs grow and digital tools become more important, cloud adoption helps healthcare providers stay efficient and prepared.
A successful migration requires careful planning. It involves meeting compliance requirements, selecting the right technology partners, testing systems thoroughly, and preparing internal teams for the change. These steps help reduce disruption and support a smooth transition.
If your organization is planning this move, working with a team that understands both healthcare systems and cloud technologies can make the process more effective. From secure cloud services and solutions to ongoing support through healthcare application development, we are here to assist at every stage.

FAQs
It depends on your system size and complexity. Smaller projects take a few weeks. Larger migrations can take months, especially with legacy systems.
Yes, if your software is cloud-compatible or can be containerized. Some older tools may need updates or partial replacements.
Possibly. Devices may need reconfiguration or middleware support. Compatibility should be checked early in the planning stage.
Support includes monitoring, security updates, backups, and system checks. Ongoing training and compliance reviews are also helpful.
Not always. External teams offering cloud consulting services can manage the migration. Internal IT leads can help coordinate.
Through validation tools, test sampling, and audit logs. It’s important to confirm that records and reports are complete and accurate.








