Delayed treatments, limited staff visibility, and scattered medical data often affect how fast and how well patients receive care. These problems may not always be visible to patients, but healthcare teams deal with them daily. The gap isn’t always in skill or equipment, it’s in information flow and timing.
This is where the Internet of Things (IoT) quietly steps in to make a difference.
IoT connects medical devices, wearables, hospital systems, and even ambulances to a common network. It gives doctors, nurses, and caregivers real-time access to data that would otherwise be missed, delayed, or lost in silos.
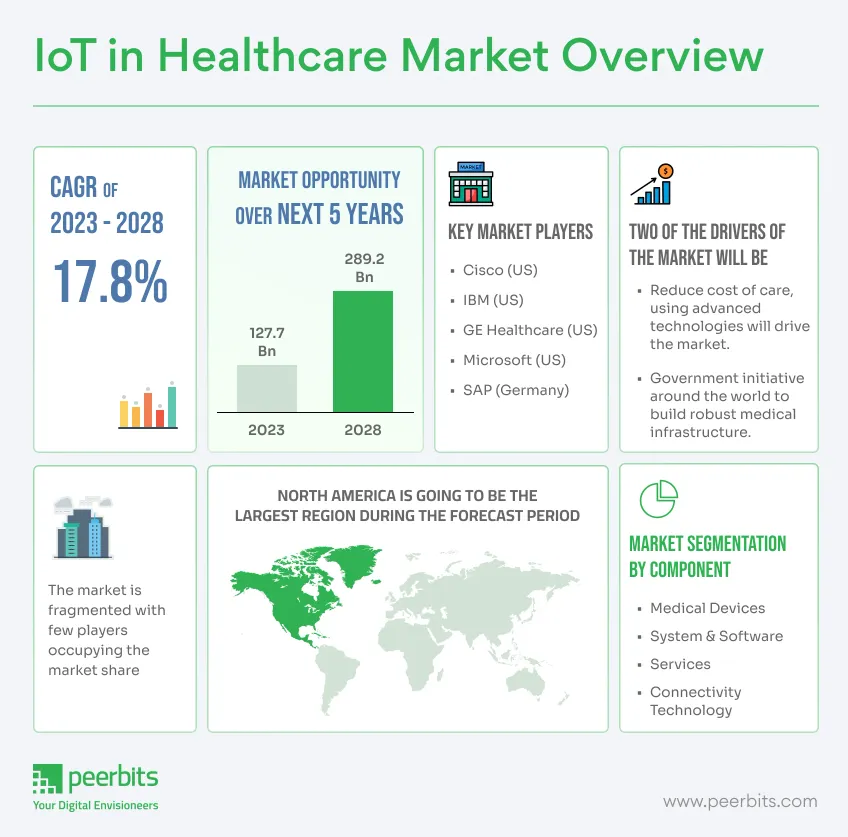
And the momentum is clearly visible. As per Precedence Research, the global IoT in healthcare market stood at USD 53.64 billion in 2024, grew to USD 65.03 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 368.06 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 21.24%.
This surge in growth reflects a shift from reactive to proactive care, from guesswork to insight-driven action. Whether it’s remote monitoring, smart beds, or digital asset tracking, IoT is helping care providers and healthcare software development companies improve outcomes while reducing pressure on healthcare systems.
In this blog, we’ll walk through how IoT is currently being used in healthcare, the key benefits it offers, and the practical challenges still standing in the way.
Let’s begin with where and how IoT fits into today’s healthcare ecosystem.
What exactly is IoT, and Why is it important In Healthcare?
In simple terms,
“IoT, or the Internet of Things, is a network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity that enables them to collect and exchange data.”
These devices are connected through the internet and create an IoT system that allows them to interact with one another and with other internet-enabled devices and services.
We can consider an IoT healthcare facility as a collection of ubiquitous computing that mainly deals with external activities.
Why IoT is important in Healthcare?
So, in healthcare, IoT-based healthcare systems collect a variety of patient data and get inputs from doctors and medical professionals. Continuous glucose monitoring for insulin pens is the best example of this.
All these devices can communicate with each other and take important actions that would provide timely help to save someone’s life. After collecting the data, an IoT healthcare device would send this critical information to the cloud so that doctors can act upon it.
From this, we can say that the potential application of IoT in healthcare can improve a patient’s health, healthcare employee productivity, and hospital workflow.
How does IoT help in healthcare processes?
Here is the workflow of IoT healthcare:
- A sensor collects data from a patient, doctor or nurse inputs data.
- AI-driven algorithms like Machine Learning (ML) are used to analyze the collected data.
- The device decides whether to act or send the information to the cloud.
- Doctors or health practitioners can make actionable and informed decisions based on the data provided by IoT healthcare solutions.
Benefits of IoT in Healthcare
The benefits of IoT in different industries are numerous, and the healthcare industry is no exception. Here are some of the top advantages of IoT in healthcare.
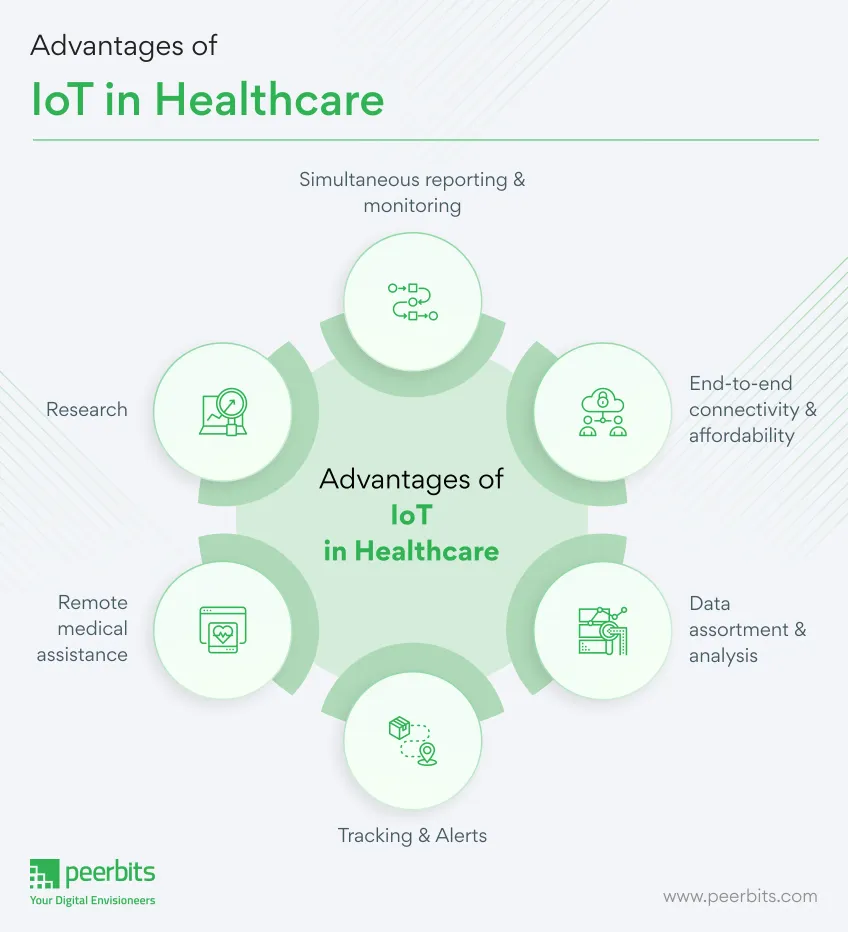
Simultaneous reporting and monitoring
Remote patient monitoring through connected devices helps track vital signs and share them instantly with doctors via smartphone apps or cloud platforms.
Remote patient monitoring also ensures that data such as blood pressure, oxygen, or sugar levels can be securely shared with authorized health partners, improving care coordination and reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
End-to-end connectivity and affordability
IoT can automate patient care workflow with the help of healthcare apps development services and other new IoT technologies, and next-gen healthcare facilities.
IoT in healthcare supports smooth data exchange, AI-driven communication, and interoperability, making care more efficient. With healthcare app development services and modern connectivity protocols like Bluetooth LE, Wi-Fi, or ZigBee, healthcare teams can detect illnesses earlier and improve treatments.
This connected setup also reduces costs by cutting unnecessary visits, improving resource use, and enabling smarter planning.
Data assortment and analysis
IoT devices gather and process health data in real time, cutting the need to store raw information. With cloud support and an identity access management solution, only authorized personnel can access sensitive reports.
Instead of handling large volumes of data manually, healthcare providers receive clear insights and analytics that speed up decisions and reduce errors.
Tracking and Alerts
On-time alert is critical in chronic conditions. Medical IoT devices gather vital signs of any disease and transfer that data to doctors for real-time tracking, while dropping notifications to people about critical parts via mobile app technology and smart sensors.

Reports and alerts give a firm opinion about a patient’s condition, irrespective of place and time.
It also helps healthcare providers to make well-versed decisions and provide on-time treatment.
Thus, IoT enables real-time alerting, tracking, and monitoring, which permits hands-on treatments, better accuracy, apt intervention by doctors and improves complete patient care delivery results.
Remote Medical Assistance
In the event of an emergency, patients can contact a doctor who is many kilometers away with a smart mobile app.
With mobility solutions in healthcare, the medics can instantly check the patients and identify the ailments on-the-go.
Also, numerous IoT-based healthcare delivery chains are planning to build machines that can distribute drugs on the basis of patient prescription and ailment-related data available via linked devices. This, in turn, will cut on people’s expenses on healthcare.
Research
IoT healthcare applications help collect large volumes of patient data quickly, which supports medical studies and new treatments. This saves both time and cost compared to manual research.
IoT-powered devices, including updated hospital equipment with smart chips, improve the quality of care while also advancing medical research.
Challenges of the IoT in Healthcare
Some key challenges to address for IoT healthcare include:
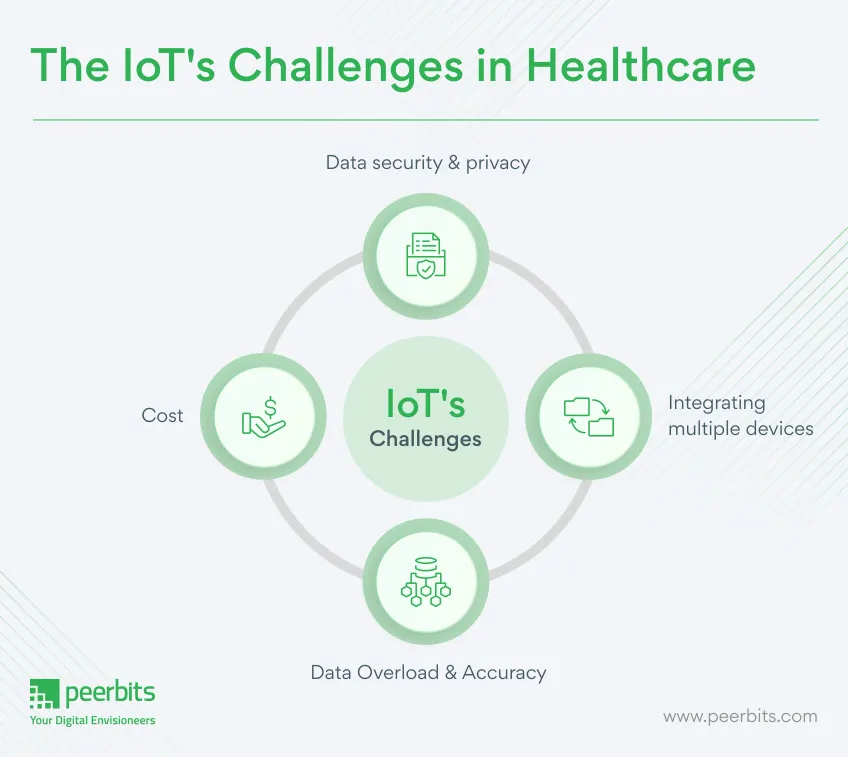
Data Security & Privacy
IoT devices capture and transmit sensitive health data in real time, but many lack proper security protocols and clear ownership regulations. This leaves patient records vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Hackers can exploit personal health information to create fake IDs, buy drugs or equipment, and even file fraudulent insurance claims.
Integration: Multiple Devices & Protocols
Implementing IoT in healthcare is challenging when devices use different communication standards. This lack of uniformity makes data aggregation difficult, slows processes, and limits scalability.
Data Overload & Accuracy
IoT devices generate massive amounts of health data, but the lack of standard protocols makes it hard to process and analyze effectively. The Internet of Things (IoT) adds to this challenge as more devices connect and record data, making it difficult for doctors to extract accurate insights. This can impact decision-making and even patient safety.
Cost
While IoT in healthcare offers many advantages, affordability remains a major hurdle. Rising healthcare costs still keep these solutions out of reach for many patients.
Use cases of IoT in healthcare
IoT in healthcare is now being used in medical settings every day. From routine monitoring to advanced treatments, here are some practical use cases making a difference:
-
Remote patient monitoring: Smart devices track vital signs like blood pressure or oxygen levels and send data to physicians in real time, reducing hospital visits and enabling timely care.
-
Disease monitoring: Patients with chronic conditions like asthma or COPD benefit from connected devices that monitor symptoms and alert caregivers of sudden changes.
-
Telemedicine: Telemedicine app development services paired with IoT devices allow patients to consult with doctors remotely.
-
Connected contact lenses: These lenses can track glucose levels or detect early signs of eye diseases, providing valuable data without invasive testing.
-
Connected drug delivery system: Automated systems deliver drugs based on real-time patient needs, reducing errors and improving treatment effectiveness.
-
Improved insurance processes: Insurance companies use IoT health data to verify claims, personalize policies, and encourage healthier lifestyles through rewards.
-
Computer vision technology: Computer vision services along with AI has given rise to drone technology which aims to mimic visual perception and hence decision-making based on it.
Conclusion
IoT has become a part of how care is delivered, managed, and improved. From remote consultations to real-time vitals tracking, IoT brings speed, accuracy, and proactive decision-making into the hands of healthcare professionals.
While the benefits are clear, security challenges remain a real concern. As more devices connect and share sensitive data, the risk of breaches and misuse increases, making security a key priority for future adoption.
Even so, the expansion continues. Wearables, ingestible sensors, and smart video pills are already showing how technology can support better outcomes. With its potential to reduce costs and push care toward prevention, IoT is moving from support tool to strategic necessity in modern healthcare.

FAQ's
Healthcare IoT devices should comply with standards like HIPAA (USA), ISO/IEC 27001, and FDA guidelines for cybersecurity. These help protect patient data and ensure the device is secure for clinical use.
Hospitals can begin with small-scale implementations like smart temperature monitors or connected inhalers, then gradually scale. Collaborating with IoT and healthcare tech specialists ensures compatibility with legacy systems.
IoT adds complexity to patient data collection. Consent must be more detailed, covering continuous data capture, remote monitoring, and third-party data sharing, all while meeting regional privacy regulations.
Yes, especially when paired with telemedicine. IoT devices like remote diagnostics and wearable trackers can offer essential services to patients in under-resourced or hard-to-reach areas.
They typically use cloud-based storage and data management systems with analytics capabilities. Partnering with cloud consulting services can help create efficient, secure, and scalable storage workflows.
Yes. With the right APIs and integration frameworks, IoT device data can sync with EHRs to provide clinicians with real-time patient updates in a centralized dashboard.








