The MEAN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, AngularJS, and Node.js) is gaining serious ground in web application development. MongoDB brings flexibility to data handling.
Node.js keeps your server active without breaks. Express.js simplifies backend routing. Angular helps build dynamic interfaces.
Many developers who once worked with the LAMP stack are now moving to MEAN, mostly because LAMP doesn’t match the current development demands. Technologies have changed, and MEAN suits projects that demand faster development, cleaner code, and modern UI.
Angular in particular helps overcome HTML’s limitations in single-page app development. If you're planning your next web application development project, MEAN might fit better than legacy frameworks.
| MEAN Stack | LAMP Stack | |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Cross-platform | Linux OS only |
| Database | MongoDB, a ‘non-relational’ database | MySQL, a ‘relational’ database |
| Programming Language(s) | Frontend—JavaScript Backend—PHP | JavaScript, back and frontend |
| Structure | Slower & limited due to its blocking structure | faster & scalable due to its non-blocking structure. |
| Technologies | MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js | Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP |
| Mainstream Backers | Google, IBM, Samsung | Oracle, Zend, Linux Foundation |
MEAN stack
Developers looking to host maximum user engagement on their web app choose the most feasible technologies and frameworks. There is a long list of technologies and MEAN stack is recipe to modern web applications. Introduced in 2014, MEAN has transformed the way the web development progresses. As mentioned above, four components in MEAN Stack are the following:
MongoDB, document database – used by your back-end application to store its data as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) documents
Express.js, a back-end web application framework running on top of Node.js
Angular, a front-end web application framework; runs your JavaScript code in the user's
browser, allowing your application UI to be dynamic
Node.js, a JavaScript runtime environment – lets you implement your application back-end in JavaScript
MEAN stack is all about JavaScript—backend development, frontend development, or server, all are done in the same programming language. Access to the database is through MongoDB's idiomatic driver. Drivers facilitate interaction using typical JavaScript concepts such as objects and async execution using either callback functions or promises. If you're looking to build scalable, end-to-end JavaScript applications, it's a smart move to hire MEAN stack developer who understands these concepts in depth. I have inserted an array of 3 objects in JavaScript:
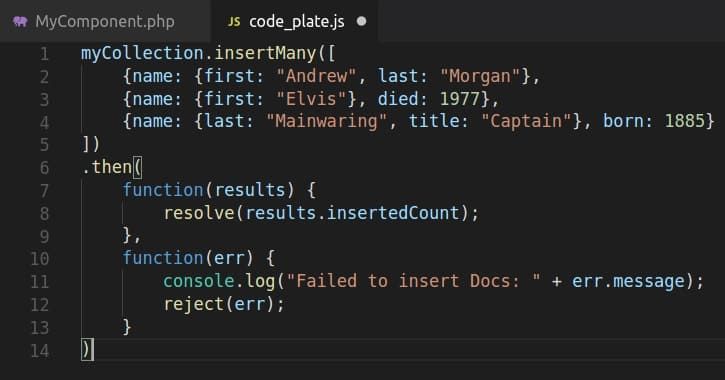
Database system: MongoDB
MongoDB has the best of the both worlds fast, scalable key-value stores of NoSQL and rich functionality of relational databases. Unlike relational database MongoDB stores BSON documents inside collections with active schemas.
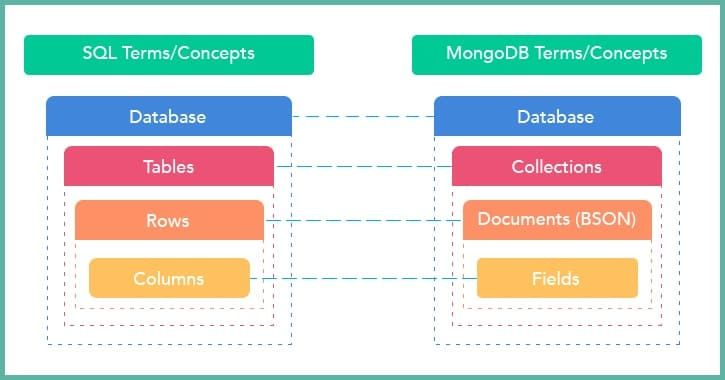
While relational databases like MySQL store data in specific rows and columns, MongoDB's document data model stores data regardless of its structure. If you want to take full advantage of this flexibility without disrupting authentication rules, data access, or indexing functionality, it’s crucial to hire MongoDB developers skilled in handling such dynamic data models. You can actively adjust the schema without interruption—trivial for swiftly scaling web applications.
Backend web framework: Express.js
Express is a web application framework that executes back-end application (JavaScript) code. Express is a module Node.js environment and runs under it.
Express handles allocation of requests to different parts of an application (or to various apps running in the same environment).
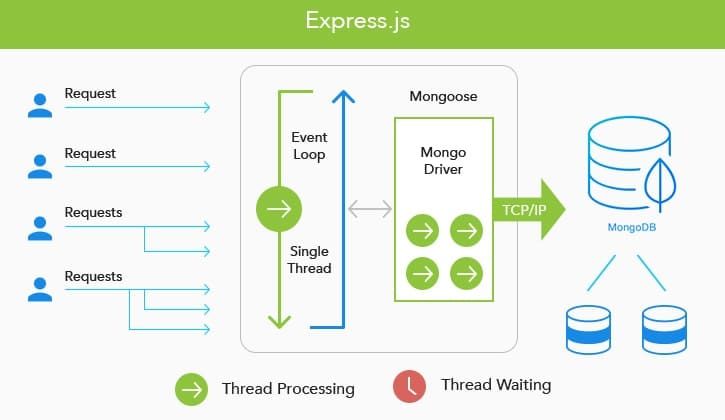
Express executes the part of a web app's code that is responsible for business logic and returns an HTML file to be compiled by a web browser. However, Express, mostly gives a RESTful APIs that the front-end can access with a single line of code.
Frontend framework: Angular
Angular render JavaScript code in a web browser’s environment to make way for reactive user interface (UI). Unlike static web forms where you have to fill in the form and hit submit, reactive UI reflects a user’s input without refreshing the entire page but only the essential components.
You implement your web app frontend as a group of components. A JavaScript code attached to an HTML template contains hooks to execute and employ the results from your JavaScript functions. Multifaceted application front-ends can be built from many simple or nested components. To ensure scalable and maintainable architecture, it's often best to hire Angular developers who can expertly structure and manage these component-based interfaces.
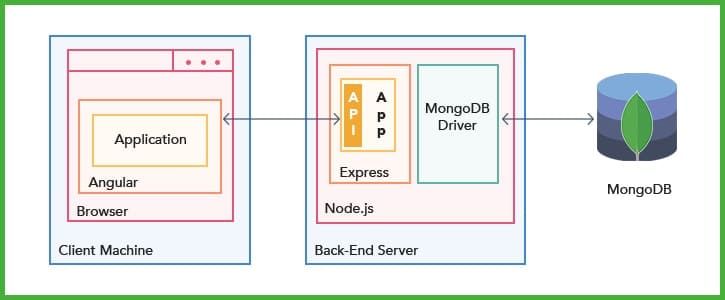
Angular application code can compile in the back-end server rather than in the frontend browser, or as a native desktop or mobile app.
Backend runtime environment: Node.js
A JavaScript runtime environment to run your back-end application with the help of Express, Node.js is based on Google's V8, a JavaScript engine that powers Google Chrome and open-source Chromium browser. Many of its modules are essential for deploying web applications on the MEAN stack – including HTTP. 3rd party modules can be installed with npm tool.
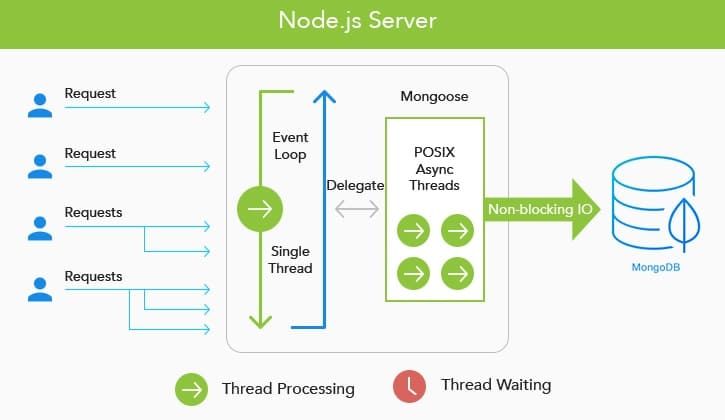
Node.js is asynchronous and event-driven. That is, an application doesn’t poll an acknowledgement to a request. It resumes other tasks in the meanwhile. Upon completion, a callback request informs the application and it can start other tasks for optimal resource utilization, which enables many parallel operations while scaling applications. MongoDB can work asynchronously too and, thus, works well with Node.js applications. To build high-performance, scalable systems like these, it’s a smart choice to hire Node.js developer who understands event-driven architecture and asynchronous workflows.
If you are still not confident about MEAN stack, we will take you through why you should be using MEAN stack for your next web development project.
Ultimate language: JavaScript

Every piece of code in MEAN stack is JavaScript. On the other hand, in LAMP stack, server-side is coded in PHP and the client side in JavaScript. A query is sent using MySQL, which is unlike MEAN stack. MongoDB is again JavaScript—it’s the binary version of JSON. In a nutshell, the same language works, client and the server side.
Cost-effective while fast and scalable
A team of JavaScript developers can code for server side and client side using MEAN stack. So, no need to hire separate teams for different technologies. The same developer can switch role between a frontend and backend developer. This will save you a lot of money. A single team for MEAN stack development. For the first time in the history of web development, a full-stack developer needs to know only one language.
Advantages of Node.js
Node.js is a crucial part of MEAN stack and is a very scalable and robust framework. Node.js is the runtime environment and is comply with non-blocking input and output. Thus, a new query is handled efficiently. In LAMP stack, the client had to direct a request for the query to be created. With Node.js, this all happens automatically.

MongoDB Advantage
MongoDB is the database web developers for hire need while managing huge amount of data. The whole thing works like OOPs and makes way for easy, effective handling.
Open-Source freedom: Edit, compile, install
Technologies that bring us MEAN stack are all open-source. That is, developers get access to the codes of each technology and can modify the core to meet their individual needs. The technologies doesn’t cost a buck to use and distribute, which means you not only can use it for personal use but also can install them on your employees personal workspaces.
Conclusion
Moving from LAMP to MEAN is a practical decision for businesses aiming to stay efficient, scalable, and aligned with modern web application development practices. It’s not just a shift in technology—it’s about simplifying workflows and building smarter systems that deliver results faster.
With JavaScript running across the stack, MEAN makes it easier for teams to collaborate and keep development streamlined. MongoDB handles data with flexibility, Angular creates dynamic user interfaces, Express.js manages backend tasks smoothly, and Node.js keeps the application fast and responsive.
If your current stack is holding back performance or creating unnecessary complexity, switching to MEAN can help you move forward with clarity and confidence.









